Trump administration’s return to the White House has brought significant changes to federal student loan policies that will impact millions of borrowers across America. If you’re among the 43 million Americans carrying student debt, understanding these policy shifts isn’t just important—it’s essential for your financial future.
These changes affect everything from monthly payment calculations to loan forgiveness eligibility, and some modifications are already taking effect. Whether you’re currently repaying loans, considering consolidation, or hoping for forgiveness, this comprehensive guide breaks down exactly what you need to know.
The Big Picture: What’s Changed Under Trump’s Student Loan Approach
President Trump’s administration has taken a markedly different approach to student loan policy compared to previous years. The focus has shifted toward fiscal responsibility, reduced government spending on loan forgiveness programs, and increased accountability for both borrowers and educational institutions.
This policy direction reflects the administration’s broader economic philosophy, but it also responds to growing concerns about the sustainability of current student loan programs. With total student debt exceeding $1.7 trillion nationally, these changes aim to create what officials call a “more balanced approach” to higher education financing.
1. Income-Driven Repayment Plan Modifications
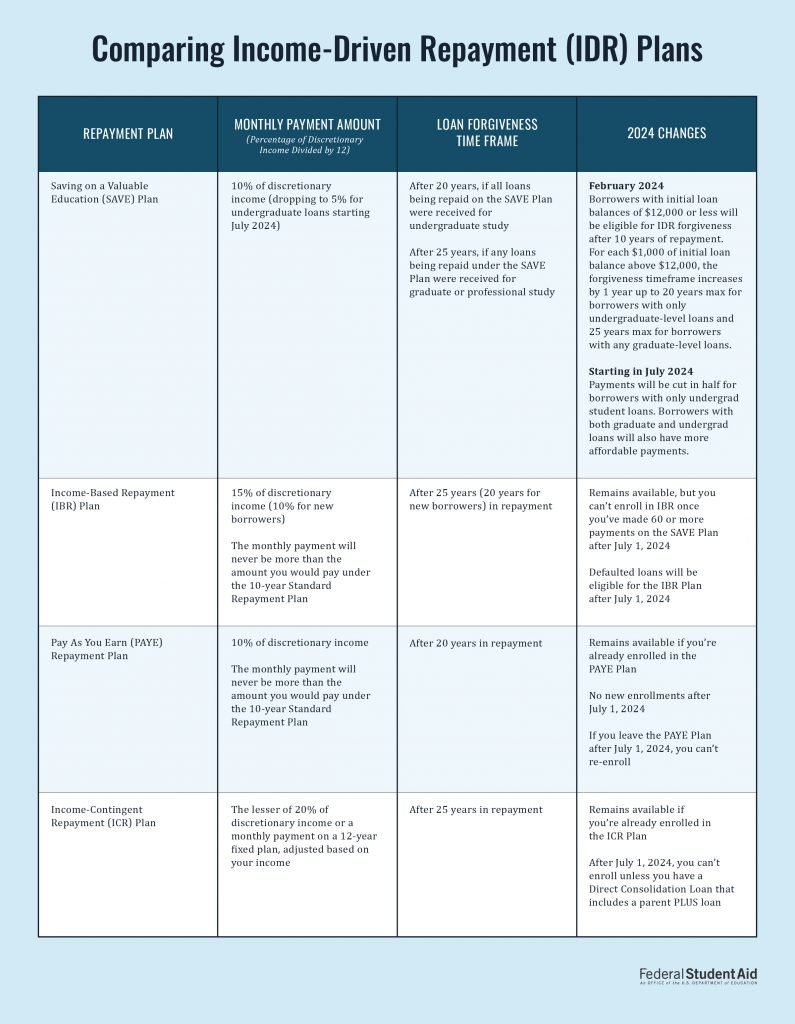
One of the most significant changes affects Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) plans, which currently help millions of borrowers manage their monthly payments based on their income and family size.
What’s Changing:
- New income verification requirements every six months instead of annually
- Stricter documentation standards for income reporting
- Modified payment calculation formulas that may result in higher monthly payments for some borrowers
- Enhanced penalties for late income recertification
Impact on Borrowers: If you’re currently on an IDR plan, expect more frequent paperwork and potentially higher payments. The administration argues this ensures payments better reflect current financial situations, but it also means more administrative burden for borrowers.
Action Steps:
- Set calendar reminders for income recertification deadlines
- Gather necessary documentation well in advance
- Consider whether your current IDR plan still makes sense under new calculations
2. Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) Program Restrictions

The PSLF program, which forgives remaining debt after 120 qualifying payments for public service workers, faces substantial modifications.
Key Changes:
- Stricter definition of “qualifying employment” that excludes some previously eligible positions
- Enhanced verification requirements for employment certification
- New annual income caps for PSLF eligibility
- Reduced flexibility in payment timing requirements
Who’s Affected: Teachers, nurses, social workers, and other public service employees may find it harder to qualify. The administration estimates these changes will reduce PSLF approvals by approximately 30%.
Strategic Considerations: If you’re pursuing PSLF, document everything meticulously and consider accelerating your qualifying payments before stricter rules take full effect.
3. Student Loan Interest Rate Adjustments
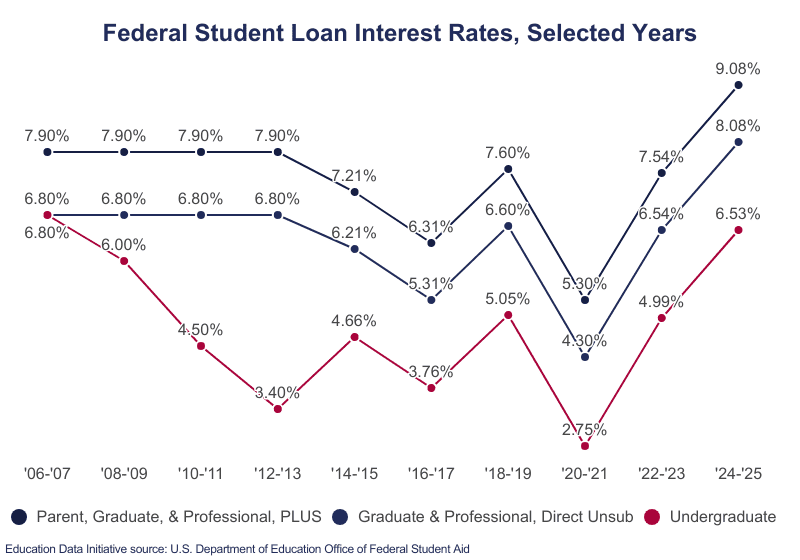
Federal student loan interest rates are seeing significant modifications under the new administration’s policies.
Rate Changes:
- New federal loans will have rates tied more closely to market conditions
- Existing variable rate loans may see increased volatility
- Graduate student loan rates face particular increases
- Parent PLUS loans will carry higher rates than previously projected
Financial Impact: Borrowers taking new loans should expect higher costs over the life of their loans. Those with existing loans may see rate adjustments at their next renewal period.
4. Borrower Defense to Repayment Program Limitations
The Borrower Defense program, which helps students defrauded by their schools, now operates under much stricter guidelines.More From Mobelwealth: 22 Legit Games That Pay Real Money (2025)
New Requirements:
- Higher burden of proof for fraud claims
- Shortened application windows
- More limited relief options
- Stricter documentation requirements
Practical Effects: Students who attended schools that engaged in deceptive practices will find it significantly harder to obtain loan forgiveness through this program.
5. Federal Student Aid Verification Process Overhaul
The FAFSA verification process has been streamlined but also made more rigorous.
Changes Include:
- Enhanced income verification through IRS data matching
- Stricter asset reporting requirements
- Increased penalties for false information
- Simplified application process with fewer questions
Student Impact: While the application process becomes easier, the verification requirements are more stringent, potentially affecting aid eligibility for some students.
6. Graduate Student Loan Program Modifications

Graduate students face particular challenges under the new policy framework.
Key Adjustments:
- Reduced borrowing limits for some graduate programs
- Stricter academic progress requirements
- Enhanced job placement tracking for graduate programs
- Modified deferment and forbearance options
Long-term Implications: Graduate students may need to rely more heavily on private loans or alternative financing methods.
7. Loan Consolidation Rule Changes
Direct Loan Consolidation rules have been modified to address what the administration sees as program abuse.
New Restrictions:
- Limited consolidation opportunities for certain loan types
- Stricter timing requirements for consolidation applications
- Modified interest rate calculation methods
- Enhanced documentation requirements
Borrower Considerations: If you’ve been considering consolidation, understand that your options may be more limited moving forward.More From Mobelwealth: The 28 Best Side Hustles: Our Top Picks to Help You Make More Money
8. Default Resolution Program Updates
The Fresh Start program and other default resolution options have been restructured.
Program Changes:
- Shortened eligibility windows for fresh start opportunities
- More stringent rehabilitation requirements
- Modified payment calculation methods for rehabilitation
- Enhanced collection enforcement mechanisms
Recovery Options: Borrowers in default will find fewer opportunities for easy resolution, making it crucial to address defaults quickly.
9. Institutional Accountability Measures
Colleges and universities face increased accountability for their students’ loan outcomes.
New Requirements:
- Enhanced job placement reporting
- Credit Card Delinquencies Drop For Second Month accreditation standards
- Financial responsibility metrics
- Potential loss of federal aid eligibility for poor-performing institutions
Student Protection: While these measures aim to protect students from predatory institutions, they may also limit options at some schools.
10. Private Loan Regulation Changes
Though federal policy doesn’t directly control private loans, new regulations affect the broader student loan landscape.
Regulatory Shifts:
- Modified bankruptcy discharge standards
- Enhanced consumer protection requirements
- Stricter lending criteria
- Improved loan servicing standards
Market Effects: Private lenders may tighten their underwriting standards, making private loans harder to obtain for some borrowers.
11. Loan Servicing Industry Restructuring
The federal loan servicing industry is undergoing significant changes.
Service Modifications:
- Consolidated servicing contracts
- Enhanced customer service standards
- Improved digital platforms
- Stricter performance metrics for servicers
Borrower Experience: While aimed at improving service, these changes may result in temporary disruptions as servicers adapt to new requirements.
12. Tax Treatment of Forgiven Loans
The tax implications of loan forgiveness have been clarified and, in some cases, made more burdensome.
Tax Changes:
- Forgiven loans may be treated as taxable income more frequently
- Reduced exclusions for certain types of forgiveness
- Enhanced IRS reporting requirements
- Modified payment plan options for tax obligations
Financial Planning: Borrowers should prepare for potential tax liabilities when loans are forgiven under any program.
13. Military and Veteran Benefits Adjustments
Service members and veterans see both positive and negative changes to their student loan benefits.
Benefit Modifications:
- Enhanced benefits for active-duty service members
- Stricter eligibility requirements for some veteran programs
- Improved coordination between VA and Education Department benefits
- Modified discharge procedures for disabled veterans
Service Impact: Overall, these changes aim to better support those who serve while ensuring program integrity.
14. Employer Student Loan Assistance Program Rules
Workplace student loan assistance programs face new regulatory requirements.
Program Changes:
- Tax treatment clarifications for employer assistance
- Reporting requirements for employers
- Enhanced coordination with federal loan programs
- Improved oversight mechanisms
Workplace Benefits: Employers may need to restructure their student loan assistance programs to comply with new regulations.
15. Future Policy Direction and Timeline
Understanding the timeline and future direction of these policies helps borrowers plan effectively.
Implementation Schedule:
- Phase 1 (January-March 2025): IDR and PSLF changes
- Phase 2 (April-June 2025): Interest rate and consolidation modifications
- Phase 3 (July-September 2025): Institutional accountability measures
- Phase 4 (October-December 2025): Full implementation of all changes
Long-term Outlook: The administration has indicated these changes represent the first phase of a broader student loan policy overhaul expected to continue through 2026.
How These Changes Affect Different Types of Borrowers
Recent Graduates
New graduates face higher interest rates and more stringent repayment requirements. Focus on securing employment quickly and consider aggressive repayment strategies to minimize long-term costs.
Public Service Workers
PSLF changes require careful documentation and may necessitate career planning adjustments. Consider whether public service remains financially viable under new rules.
Graduate Students
Expect reduced borrowing capacity and higher costs. Explore alternative financing options and consider the return on investment for graduate education more carefully.
Struggling Borrowers
Fewer safety nets mean proactive communication with servicers becomes crucial. Explore all available options before falling behind on payments.
Parent Borrowers
PLUS loan changes affect family college financing strategies. Parents should reassess their ability to take on additional debt and consider alternatives.
Essential Action Steps for All Borrowers
Immediate Actions (Next 30 Days)
- Review your current loan status through your servicer’s website
- Update contact information with all loan servicers
- Gather financial documents for potential income recertification
- Research your repayment options under new rules
- Consider consolidation if beneficial under current rules
Medium-term Planning (Next 6 Months)
- Reassess your repayment strategy based on new policies
- Explore employer assistance programs while they remain available
- Consider refinancing options if you have good credit
- Plan for potential tax implications of any forgiveness
- Stay informed about ongoing policy changes
Long-term Considerations (Next 1-2 Years)
- Adjust career planning if pursuing PSLF
- Reevaluate graduate school plans given new borrowing limits
- Consider accelerated repayment to minimize interest costs
- Build emergency funds to handle payment disruptions
- Monitor credit scores as policies affect your financial profile
Staying Informed and Prepared
The student loan landscape continues evolving rapidly. Here’s how to stay ahead:
Official Resources:
- Federal Student Aid website (studentaid.gov)
- Your loan servicer’s website and communications
- Department of Education policy announcements
- IRS guidance on loan forgiveness taxation
Professional Guidance: Consider consulting with a financial advisor who specializes in student loans, especially if you have complex situations involving multiple loan types or repayment strategies.
Regular Monitoring: Set up alerts for policy changes and regularly review your loan status. Small changes in policy can have significant long-term financial impacts.
The Bottom Line
Trump’s 2025 student loan policies represent a fundamental shift toward increased borrower responsibility and reduced government spending on loan forgiveness programs. While these changes aim to create more sustainable programs, they also place greater burden on individual borrowers to manage their debt effectively.
Success under these new policies requires proactive planning, careful documentation, and strategic decision-making. Borrowers who adapt quickly to these changes and take advantage of remaining opportunities will be better positioned for financial success.
The key is understanding that the old strategies may no longer work under the new policy framework. Whether you’re just starting to repay loans or have been managing student debt for years, now is the time to reassess your approach and align your strategy with the new reality of student loan policy.
Remember, while these changes may seem overwhelming, they also create opportunities for borrowers who are willing to take control of their financial futures. By staying informed, acting proactively, and making strategic decisions, you can navigate these changes successfully and achieve your goal of becoming debt-free.
This article provides general information about student loan policy changes and should not be considered personalized financial advice. Consult with qualified professionals for guidance specific to your situation.













Loading comments...
Leave a Comment(Login required)